The CPU and RAM work together through a memory bus, where data, access, and control lanes are involved. They interact by the CPU fetching, decoding, and executing programs, while the memory stores the data and programs in use.
This collaboration allows the CPU to access and manipulate the necessary data for program execution. RAM is connected to the CPU through the memory bus, allowing for seamless data transfer and storage. The CPU speed and memory controller on the motherboard also play a role in determining the effective RAM speed.
Credit: homepage.cs.uri.edu
Understanding The Cpu And Ram
The CPU and RAM work together in a computer system to execute programs and store data. The CPU processes instructions using the fetch-decode-execute cycle, while the RAM provides temporary storage for the data and programs in use. They are connected through a memory bus.
In One Lesson: How Computers Work
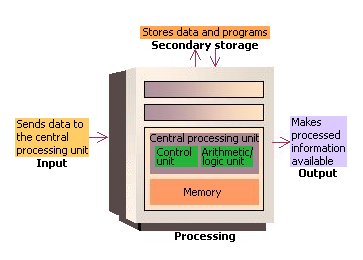
Understanding the CPU and RAM is essential for gaining insight into how computers function. The CPU, or Central Processing Unit, is often referred to as the “brain” of the computer. It carries out instructions and performs calculations necessary for various tasks. On the other hand, RAM, or Random Access Memory, is a type of computer memory that temporarily stores data that the CPU needs to access quickly. In this article, we will explore how the CPU and RAM work together seamlessly to ensure the smooth operation of a computer system.How Computers Work
To comprehend the interplay between the CPU and RAM, let us first delve into how computers operate. When a computer is powered on, the CPU starts executing instructions stored in the computer’s memory. These instructions are fetched, decoded, and executed in a continuous cycle known as the fetch-decode-execute cycle. The CPU fetches instructions from memory, decodes them to understand their meaning, and performs the necessary actions accordingly.Understanding The Cpu
The CPU comprises several components that collectively enable it to carry out its tasks effectively. These components include registers, cache memory, and the arithmetic logic unit (ALU). Registers are small storage areas within the CPU that facilitate the quick access and storage of data. The cache memory, which is faster than main memory but smaller in size, is employed to store frequently used instructions and data. The ALU performs arithmetic and logical operations on the data processed by the CPU.Exploring Ram
RAM plays a pivotal role in the functioning of a computer system. It serves as a temporary storage location for data that the CPU requires immediate access to. Unlike the hard drive, which stores data persistently, RAM is volatile memory, meaning it loses its contents when the computer is turned off. RAM allows the CPU to quickly load and retrieve data, significantly enhancing the computer’s overall performance.The Cpu-ram Relationship
The CPU and RAM collaborate through a memory bus, a communication channel that connects the CPU to the memory module. The memory bus consists of data, access, and control lanes, which enable the CPU to read and write data to and from RAM. When the CPU needs data or instructions, it sends requests through the memory bus, and the RAM promptly responds by delivering the required information. This constant interaction between the CPU and RAM ensures that data is readily available for processing and execution. To summarize, the CPU and RAM work hand in hand to facilitate the efficient functioning of a computer system. The CPU processes instructions and performs calculations, while RAM provides the necessary data for these operations. Understanding this synergy between the CPU and RAM is crucial for comprehending the intricate workings of computers.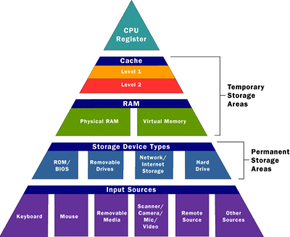
Credit: computer.howstuffworks.com
The Cpu And Ram Relationship
Understanding the relationship between the CPU and RAM is crucial in comprehending how a computer system operates efficiently. The CPU, also known as the Central Processing Unit, is considered the brain of the computer, responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations. On the other hand, RAM, or Random Access Memory, functions as the computer’s short-term memory, storing data that is currently in use by the CPU. Together, the CPU and RAM work in harmony to process data and ensure smooth operation.
Connection Through Memory Bus
The CPU and RAM establish a connection through a memory bus. The memory bus acts as a communication channel, facilitating the exchange of data, access signals, and control information between the CPU and RAM. This bus consists of different lanes, each serving a specific purpose. The data lanes allow the transmission of data between the CPU and RAM, while the access lanes determine how the CPU accesses specific memory locations. Lastly, the control lanes manage the flow of communication, ensuring synchronization between the CPU and RAM.
Interaction With Each Other
Once connected, the CPU and RAM interact with each other in a coordinated manner to carry out tasks efficiently. When the CPU needs data, it sends a request to the RAM through the memory bus, specifying the memory location. The RAM then retrieves the requested data and sends it back to the CPU for processing. Similarly, when the CPU needs to store data, it sends the data to the RAM through the memory bus, which stores it in the appropriate memory location. This constant interaction between the CPU and RAM allows for rapid data access and manipulation, ensuring seamless operation of the computer system.
How The Cpu Controls Ram
The CPU controls RAM through a memory bus, which connects the CPU or memory controller to the RAM. The CPU sends and receives data to and from RAM, allowing it to execute programs and store temporary data. This close coordination between the CPU and RAM ensures efficient performance in computer systems.
Ram Speed Control By Motherboard
The speed at which RAM operates is controlled by the motherboard, which acts as the intermediary between the CPU and RAM. The motherboard determines the clock speed and the timings for accessing the RAM modules. It also provides the necessary voltage and electrical connections for proper communication between the CPU and RAM. The motherboard’s BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) contains settings that allow users to adjust the RAM speed and timings, ensuring maximum performance and compatibility.Role Of Cpu In Ram Speed
The CPU plays a crucial role in determining the speed at which RAM functions. The CPU sends requests to the RAM to fetch data and instructions needed for executing programs. It controls the flow of information between itself and the RAM by generating signals and coordinating the transfer of data. The CPU also controls the memory controller, which manages the access and retrieval of data from the RAM. By optimizing the memory controller and its interactions with the RAM, the CPU can enhance the overall speed and efficiency of the system. In summary, the CPU controls the RAM by sending requests for data and instructions, coordinating the transfer of information, and optimizing the memory controller. The motherboard, on the other hand, controls the speed and timings of the RAM, ensuring optimal performance and compatibility. Together, the CPU and RAM work harmoniously to process and store data, enabling the smooth operation of the computer system.
Credit: robots.net
Frequently Asked Questions For How Do Cpu And Ram Work Together?
How Is Ram Connected To The Cpu?
RAM is connected to the CPU through a memory bus, which includes data, access, and control lanes. The CPU and RAM work together to run programs, with the CPU executing programs using the fetch-decode-execute cycle, while the memory stores the data and programs in use.
How Does Cpu And Main Memory Work Together?
The CPU and main memory in a computer system work together. The CPU runs programs using the fetch-decode-execute cycle, while the memory stores the data and programs currently in use. They are connected through a memory bus, which contains data, access, and control lanes.
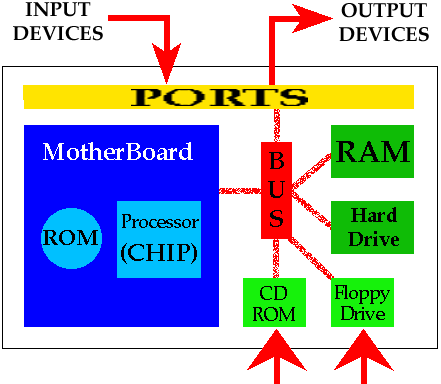
RAM and ROM are also connected to the CPU through the memory bus, while cache memory sits between the memory bus and the CPU. The CPU does not directly control the speed of RAM, as it is primarily determined by the motherboard’s memory controller.
How Does Ram Rom And Cpu Interact With Each Other?
RAM, ROM, and CPU are connected through a memory bus. They don’t directly interact with each other. The CPU can read from both RAM and ROM, but it can only write data to RAM. Cache memory sits between the CPU and the memory bus, acting as fast internal memory.
Does The Cpu Control The Ram?
No, the CPU does not control the RAM directly. The motherboard’s memory controller determines the maximum speed at which the RAM can operate, but the CPU also plays a role in supporting the RAM speed specified by the motherboard.
Conclusion
To put it simply, the CPU and RAM work hand in hand to ensure the smooth functioning of a computer system. The CPU serves as the brain of the computer, executing programs and performing calculations, while the RAM acts as the temporary storage for data that the CPU needs to access quickly.
Together, they create a seamless connection that allows for efficient processing and optimal performance. Understanding how these components work together is crucial in maximizing the capabilities of your computer.